Definition of Heat Treatment
Purpose of Heat treatment
- To Refine or Change Grain Structure
- To Remove or Realise internal stress which was produce during hot or cold working.
- Improve machinability
- Improve mechanical properties i.g ductility, hardness, toughness
- To improve magnetic and electric properties.
- To produce a hard surface on ductile material.
- To change the chemical composition.
- To increase resistance to heat and corrosion.
Classification of Heat treatment processes
- Annealing process
- Normalizing process
- Hardening process
- Tempering process
- Case hardening or Carburising process
- Cyaniding process
- Nitriding process
- Surface hardening process
- Diffusion coating process
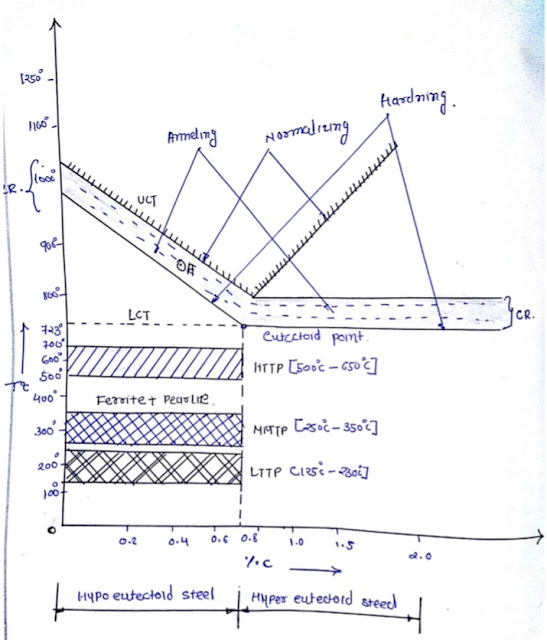
1. Annealing process
Annealing Process consists of heating metal or job to a temperature slightly above the critical range [Approx 30° to 50°] and cooling slowly in the surface with heat shut off.
Note: Heating temperature depends open the % of carbon content in metal or job
Purpose of Annealing Process
- To produce refine grain structures.
- To release internal stresses.
- To reduce hardness
- To increase ductility
- To soften the metal for increasing machinability.
Application of Annealing process
To produce desire properties of metal or job annealing process is carried out after hot and cold working.
Types of the Annealing process
- Full Annealing process
- Sub-critical annealing process
- Iso-thermal Annealing process
- Spherioding Annealing process
- Diffuse Annealing process
2. Hardening process
hardening consists of heating a metal or job at hardening temperature and holding it that temperature and quickly cooling by bathing in water, oil or salt bath
Note: hardening temperature depends upon % of the carbon contained in metal or job
Process
- Step 1: preparing metal or job for hardening process, i.e. remove oil, Greece, wax, cotton waste, seals from job
- Step 2: A heating job at hardening temperature, i.e. above 30 to 50 degrees centigrade of critical range.
- Step 3: holding the job, i.e. 1 minute for 1mm thickness
- Step 4: cool down it rapidly / quenching it either bathing in water, oil or salt bath.
- Step 5: thus hardening is carried out this way
What is the purpose of brine solution water oil and air used in the heat treatment process?
Ans: The Purpose of Brine solution and air are to Harden the Metal which is heated at the Crystallization Temperature and rapidly fallen to low temperature.
Result of the hardening process
• Here Austenite present in the job is converted into martensite structure.
Application of hardening process
The hardening process is done for the following method.
- Exo blade
- Chisel
- Shear machine blade
- Different cutting tool, such as rammers, cutters
3. Carburising Process [Case hardening process]
the carburising process is also known as case hardening process.
The case hardening process is an old process for hardening on the job.
On this basis of carbon-rich substance used in this process, the case hardening process is classified as below
- 1. Solid carburising process
- 2. Liquid carburising process
- 3. Gas carburising process
1. Solid carburising process

Usually, 0.1% carbon penetrate in 1 hour, and the surface of the job is converted into high carbon steel.
2. Liquid carburising process

The parts which are to be carburised are placed in a liquid salt bath of molten salt containing sodium carbonate, sodium chloride bath for a particular time.
Usually, 0.1% carbon penetrate in 2 hours and about 0.5mm thickness.
3. Gas carburising process

Advantages of liquid gas carburising process
- These processes are faster than the solid carburizing process
- Scales are not formed.
Disadvantages of solid carburising process
Scales are produced in solid carburizing process.
Application of Gas carburizing process
For producing wear resistance on the jobs, e.g. gears, cams, piston ring, etc.
4. Tempering process
Quenching of high carbon steel causes the formation of martensite structures which are hard and durable, but they are brittle
It is defined as a process in which hardened steel is heated to a temperature to a temperature below the critical temp. To transform the hard and brittle martensite into ferrite and cementite.
In this process ductility and toughness achieved by in cost of strength
Based on the heating condition, it is classified as below.
- 1. LTTP [Lower temperature tempering process] : 150° to 250°
- 2. MTTP [Medium temperature tempering process] : 350° to 425°
- 3. HTTP [High temperature tempering process] : 500° to 650°
Advantages of the tempering process
- It reduces the brittleness of hardened steel.
- It improves toughness and ductility.
- It is used to reduce internal stress.
5. Nitriding Process
This process involves heating of steel approx 650° temperature and holding it in the atmosphere of ammonia for some time.
The nitrogen from ammonia is penetrated into the surface of the job and form a tough coating on the job.
Hardness is achieved 1000 BHN in thickness 0.7 mm during 100 hours
Advantages of Nitriding Process
- This process improves corrosion resistance
- It improves tough hardness
- After this process job is not required any machining process
- Not required any other treatment After this process.
- No scales are formed.
Disadvantages
- This process is very costlier and time-consuming compared to another process
6. Surface Hardening process
It is classified as below
1. Flame hardening process

Inflame hardening stress is not developed due to localised heating, and the chance of cracking and distortion is reduced.
2. Induction hardening

In this process, we get a hard and wear-resistant surface with softcore in steel.
The process involves induction heating.
In this process job which too is hardened is placed into an induction coil. Coil comprises several turns of copper tube.
High-frequency current to be fed in the coil so that eddy current produced in job metal, and it is quickly heated to hardened temperature.
7. Cyaniding process
This is a special case hardening process in which the mild steel absorbs carbon and nitrogen to obtain a hard surface.
The component to be hardened immersed in a bath of sodium cyanide at a temperature of 400° c.
The component is quenched either by water or oil.
FAQs Section
What is meant by heat treatment process?
Answer: Heat treatment may be defined as an involving control heating and cooling of metals or Alloys at a Solid-state to produce the desired change in properties.
Which Processes done on gear after heat treatment in order to assemble in the gearbox?
Answer: Type of Processes is Depend Upon Functioning of Gear, But common Proceesees that to be carried out after Heat Treatment is Some Thermal And Mechanical Process, and Sub Zero Treatment and Tempering Process to get desire Degree of Hardness.
In which heat treatment process cooling is done freely in the air?
Answer: Annealing Process is the HT process in Which Metal/Job is Heated above the Critical Temperature of Metal/Job and Cool Slowly in Free Air
Why physical properties of metal does not change in heat treatment process?
Answer: Heat Treatment process is carried out to get desire properties of Metal or Job, In heat treatment process is Metal heated to Crystallization Temperature for change its grain Structure. Physical properties were not changed by Heat Treatment process

